Telemedicine Defined: What Is It And How Does It Work In Practice?
Share
Learn about the origins of telemedicine and the workflows that help healthcare providers effectively treat patients.
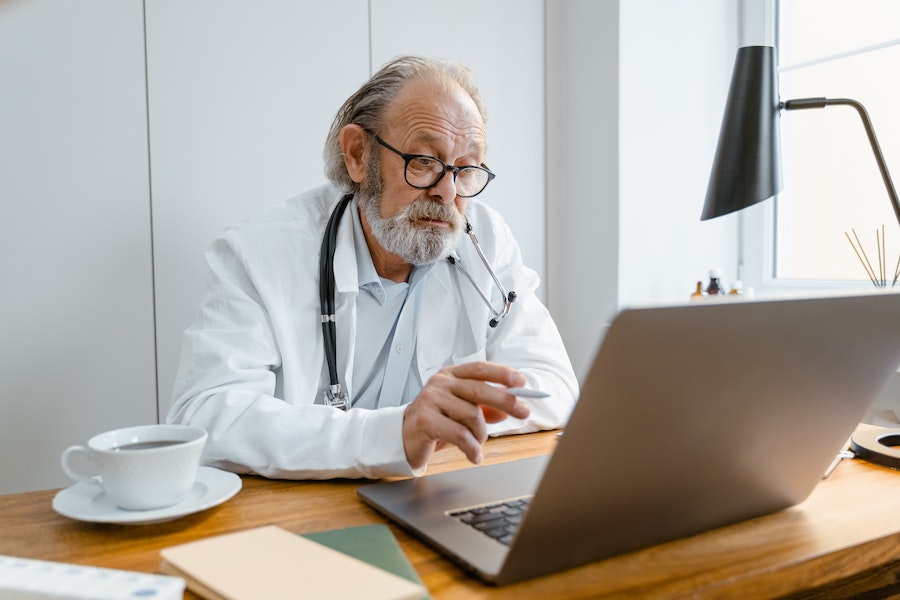
Telemedicine has become an irreplaceable part of healthcare, and it isn’t going away any time soon. Its uses range from online therapy to areas such as cardiology and neurology, improving patient outcomes. According to a McKinsey survey, 76% of patients expect telemedicine to move forward and are eager to access more healthcare services remotely. But what is telemedicine? Let’s learn what it is and see how it’s applied in today’s healthcare practices.
What Is Telemedicine?
Let’s start by defining telemedicine and its scope to better understand the areas of its application. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, telemedicine can be described as the means to offer virtual healthcare services using secure software.
The use of telemedicine dates back to 1948, when radiologists from Pennsylvania shared radiologic images using a phone connection. However, the term itself was first mentioned only in the 1970s by neurologist Thomas Bird.
When Is Telemedicine Applied?
Though healthcare practitioners considered telemedicine at its very start to be helpful only for treating patients in remote locations, nowadays, the range of areas where telemedicine is applied is much wider than that. Telemedicine is used in healthcare for:
- live communication with healthcare providers
- secure messaging, file, and document exchange
- remote patient monitoring
- prescription management
- follow-ups after in-person visits
All these applications have become possible as the functionality of telemedicine applications grows.
How Does Telemedicine Work?
The telemedicine workflow is obviously different from the workflow for in-person visits, requiring more attention to the technical side of patient care and communication aspects as well as data security. Let’s check out the best practices that healthcare specialists can use to build a successful workflow that benefits both them and their patients.
The American Medical Association has developed an approach to fit most virtual healthcare practices while possessing enough flexibility to accommodate the differences of medical practices. Let’s check it out.
Online visit workflow
The workflow always starts with obtaining the patient’s consent for telemedicine services and scheduling an appointment with the specialist.
Appointment planning
Some healthcare providers use software that allows patients to book an appointment with a specialist. In other cases, clinicians schedule an appointment themselves or ask an administrator to do this for them if the scheduling system is centralized and not automated.
It’s a good practice to send the patient a friendly reminder about the time of an appointment beforehand so they’ll be prepared. Besides, this effectively reduces the no-show rate.
When the online visit is about to start, the patient should receive a link to the appointment to join it from their device.
Online visit
The quality of virtual visits depends not only on the healthcare provider’s experience and skill but also on the connection quality. Before the visit starts, the patient has to:
- receive the appointments reminder
- confirm the appointment
- log in to the telemedicine portal
- test the connection
If there is an administrator responsible for video visits, they have to:
- collect a copay
- collect documents and patient consent
- admit the patient to the virtual platform
However, there are telemedicine platforms that offer online payment integration and allow patients to join a video conference only after payment is confirmed, so no admin is required. Another option you might find in your software for telemedicine is electronic document sharing functionality that will let you get completed consent forms before the visit as well as be notified when a form or a document is signed and shared with you.
As a specialist, you have to join the video conference on time, conduct a virtual visit, and complete all necessary documentation afterwards. Additionally, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommends making a follow-up, sending your patient a visit summary, and offering a form for giving anonymous feedback.
Online visit best practices
Now that you’re aware of the general workflow, let’s learn about recommended practices to avoid technical issues or miscommunication between you and your patient.
Tips to consider when preparing for an online visit:
- Find out if your license allows you to provide services in the area where your patient resides
- Set your schedule according to your work hours
- Make sure to have at least a five-minute break between video conferences
- Ensure your internet connection is stable and that your camera and headset are working
- Take care of options for appointment rescheduling and cancellation
- Use secure HIPAA-compliant software for video visits
- Adjust the workflow to your needs and keep to it
Final Thoughts
Now you know how telemedicine works and can create your own workflow that will help you more easily provide virtual healthcare. Make sure to follow these recommendations in order to successfully assist your patients when they need your help.